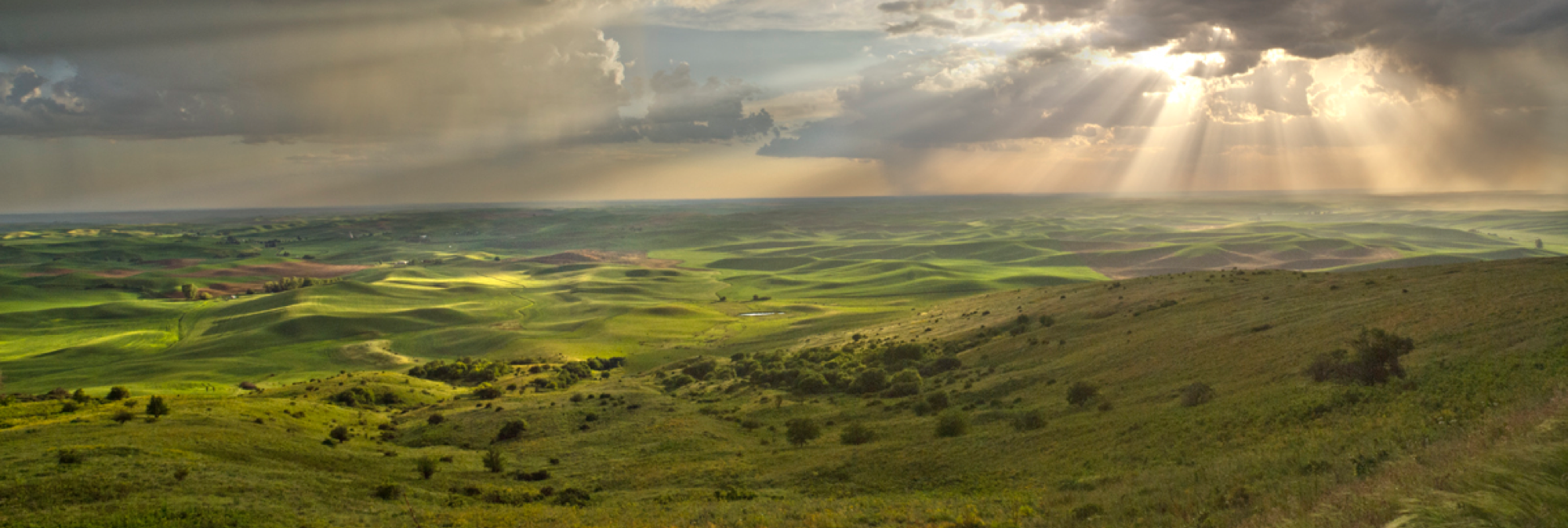
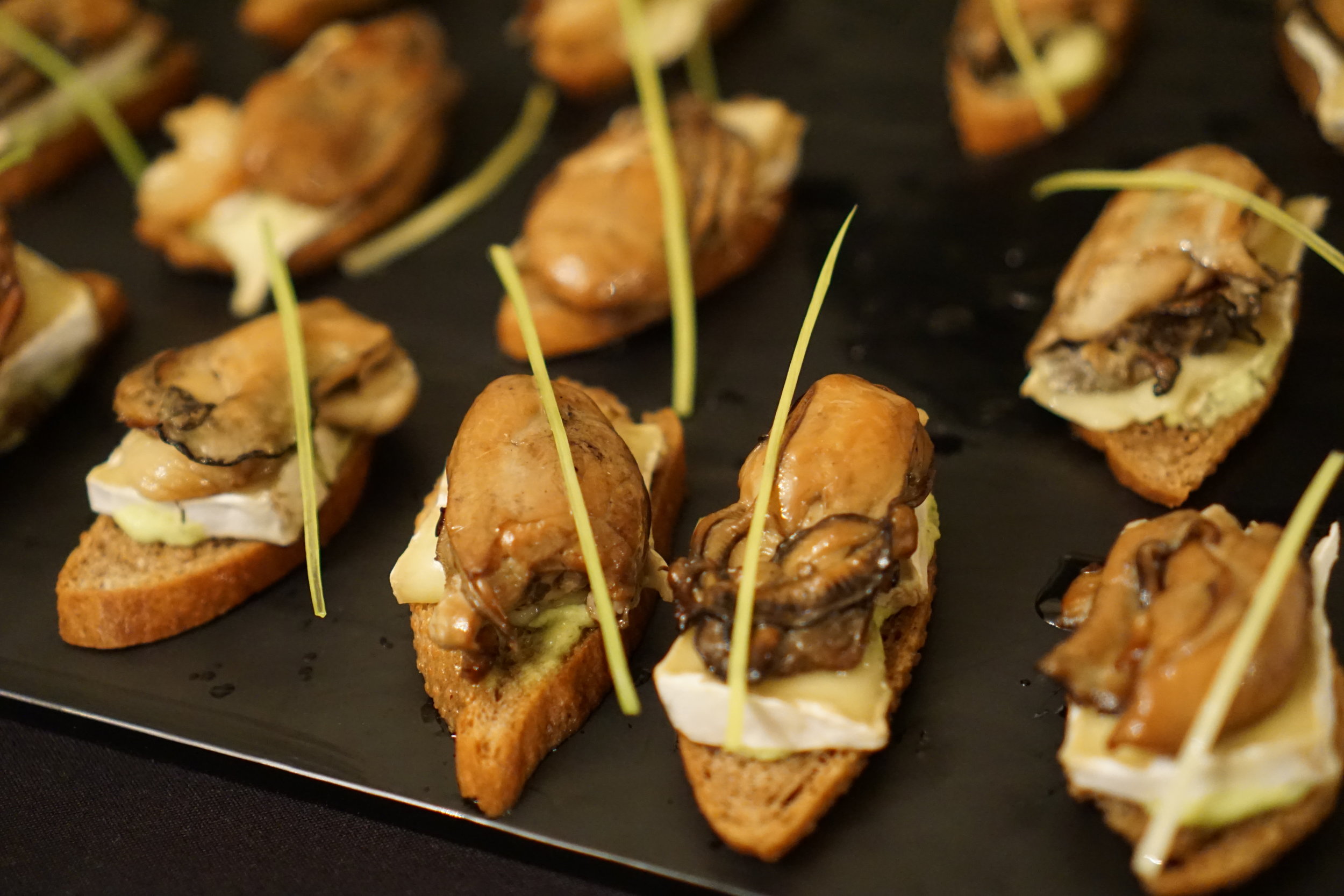
I was not surprised when famed culinary host Guy Fieri of the Food Network’s hit TV show “Diners, Drive-Ins and Dives” selected Richland’s Ethos Bakery to feature for an upcoming episode. Ethos founders Angela Kora and Scott Newell manage one of our areas most popular eateries and one trip inside their attractive space offers proof through aroma and flavor of some of the finest breads, soups, and pastries available anywhere in the region. Small wonder Angela and Scott and their talented team were accorded such an accolade. We at Palouse Heritage were especially pleased because we have long been supplying Ethos with heritage grains like Crimson Turkey wheat and Purple Egyptian barley which they mill on site for the freshest baked products possible.
Ethos Bakery & Café Culinary Treasures; Richland, Washington
I first learned about Ethos after meeting Angela at one of the annual “Grain Gatherings” sponsored by Washington State University at their Mt. Vernon Research Center north of Seattle. These convocations draw participants from across the country while others hail from Europe and Australia. It used to be that use of agrarian folksayings, recounting tales of Old and New World seasonal farm labors, and harvest work songs were the obscure domain of cultural historians and ethnologists, but burgeoning interest in such topics is evident in sustainability and food sovereignty movements here and throughout the world. At a recent Grain Gathering session, groups toured test plots of heritage White and Red Lammas wheats, Scots Bere barley, and Lincoln oats, and learned about methods and marketability of artisan breads, craft brews, and other specialty food and beverage products. Even names of event sponsors suggest Old World associations—the Bread Baking Guild, King Arthur Flour, and Wood Stone, a custom builder of stone hearth ovens.
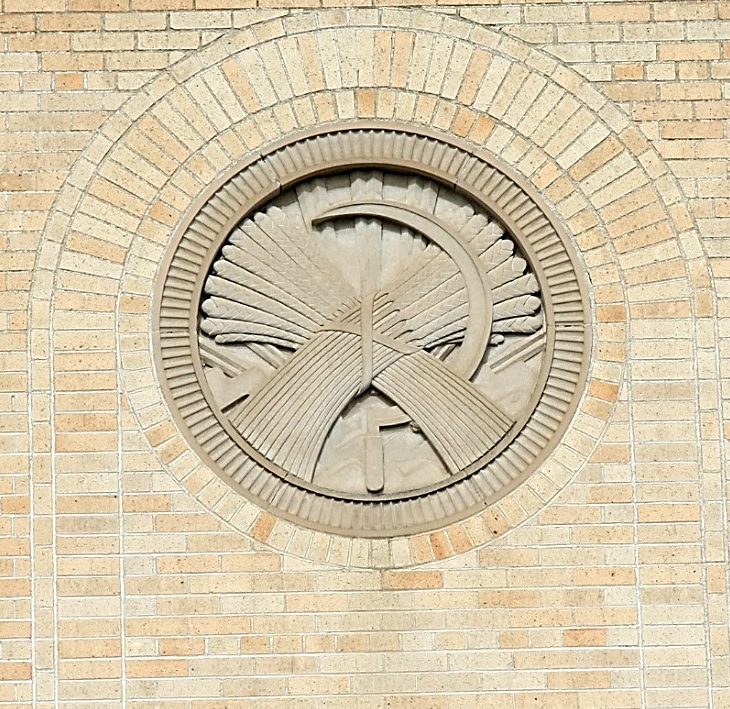
Conference presenters shared lines by the sixteenth century agrarian poet Thomas Tusser, and showcased a “Harvest Heritage” exhibit of art based on rural themes by plein air French Impressionists, American Realists, the Russian Itinerants. American folk art was represented in the once familiar Harvest Star quilt design and nineteenth century steel engravings of field workers wielding sickles. A notable modern depiction of this ancient tool is the sculpted stone bas-relief roundel carved by an unidentified New Deal era sculptor in 1941 for the Adams County Courthouse in Ritzville, Washington. Agricultural folklorist and artist Eric Sloan considered the crescent-shaped sickle in all its variations over time to be the most beautiful implement ever crafted.
Grain Sheaf Bas-relief (1941), Adams County Courthouse; Ritzville, Washington
Simple ancient depictions of sickle-bearing field workers gave way in a blended gradualism to medieval and early modern images of scythe-swinging harvesters. The social contract that had long governed and guided enduring social systems changed little until the nineteenth century. Inventions sparked by the Industrial Revolution led to the gradual replacement of sickles and scythes with mechanical reapers. This advancement in agricultural technology greatly relieved the arduous labor of harvest fields, but also compounded pressures of urban growth throughout the great grain growing nations of Europe and the America.
The horse-powered reaper developed by American Cyrus McCormick in the 1830s featured a moveable bar of small sickle sections that effectively cut grain stalks which fell onto a platform for binding and threshing. Just like anyone can enjoy today at Ethos Bakery & Café, exceptionally flavored heritage grains like Crimson Turkey were routinely held back by families to mill at home for delicious breads and other baked goods. Community elder Donald Reich of Colfax, Washington, recently told me that he remembered his immigrant father driving all the way to the Pataha Mill near Pomeroy to get their wheat ground into flour. How convenient we can go to places like Ethos and experience what they knew to be a treasure.